How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to crucial infrastructure inspections. Mastering drone operation isn’t just about understanding the controls; it’s about embracing a responsible and safe approach. This guide will take you through the essential steps, from pre-flight checklists and safety procedures to advanced flight maneuvers and legal compliance, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to fly responsibly and achieve stunning results.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From pre-flight checks to mastering maneuvers, understanding the material presented there will significantly improve your drone piloting skills and ensure safe operation.
We’ll cover the fundamental aspects of drone control, navigation techniques, flight planning strategies, and essential maintenance procedures. You’ll also learn about relevant regulations and best practices to ensure your drone flights are both successful and legally sound. This comprehensive guide aims to transform you from a novice into a confident and capable drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes risks and ensures the drone is in optimal condition for flight. This section details the necessary steps and safety considerations.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection of the drone and its components is essential. This involves visually checking for any damage to the propellers, arms, body, and camera. Battery levels should be verified, ensuring sufficient charge for the planned flight duration. Furthermore, the GPS signal strength and the connection between the drone and its remote controller should be confirmed.
Finally, all necessary safety features, such as emergency stops, should be tested.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount. These regulations vary by location, so it’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules in your area. Generally, maintaining a safe distance from people and property, avoiding flying over crowds or sensitive areas, and always keeping the drone within visual line of sight are key aspects of responsible operation.
Additionally, being aware of weather conditions and avoiding flight during adverse weather is crucial for safe operation.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
| Hazard | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Propeller strike | Maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles. |
| Battery failure | Use high-quality batteries and regularly check their condition. |
| Signal loss | Fly within the effective range of the controller and maintain a clear line of sight. |
| Adverse weather | Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding the basic controls and navigation methods is fundamental to operating a drone effectively and safely. This section explains the key controls and different flight modes.
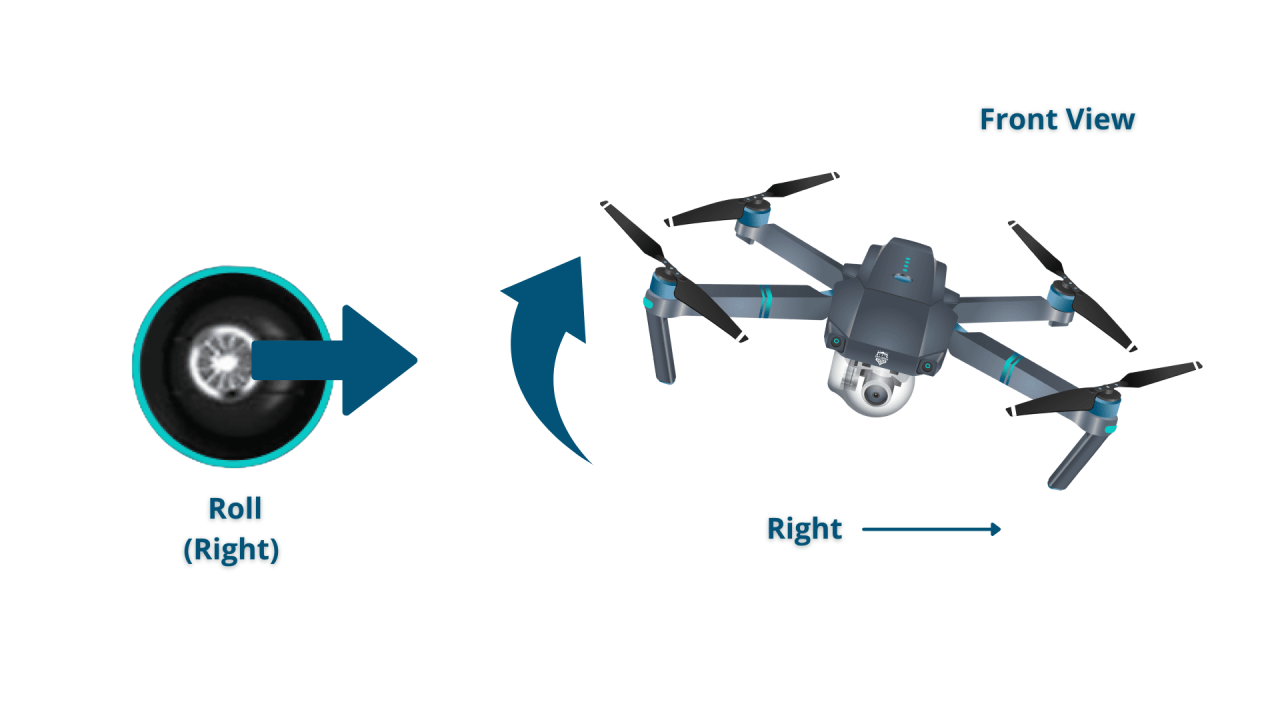
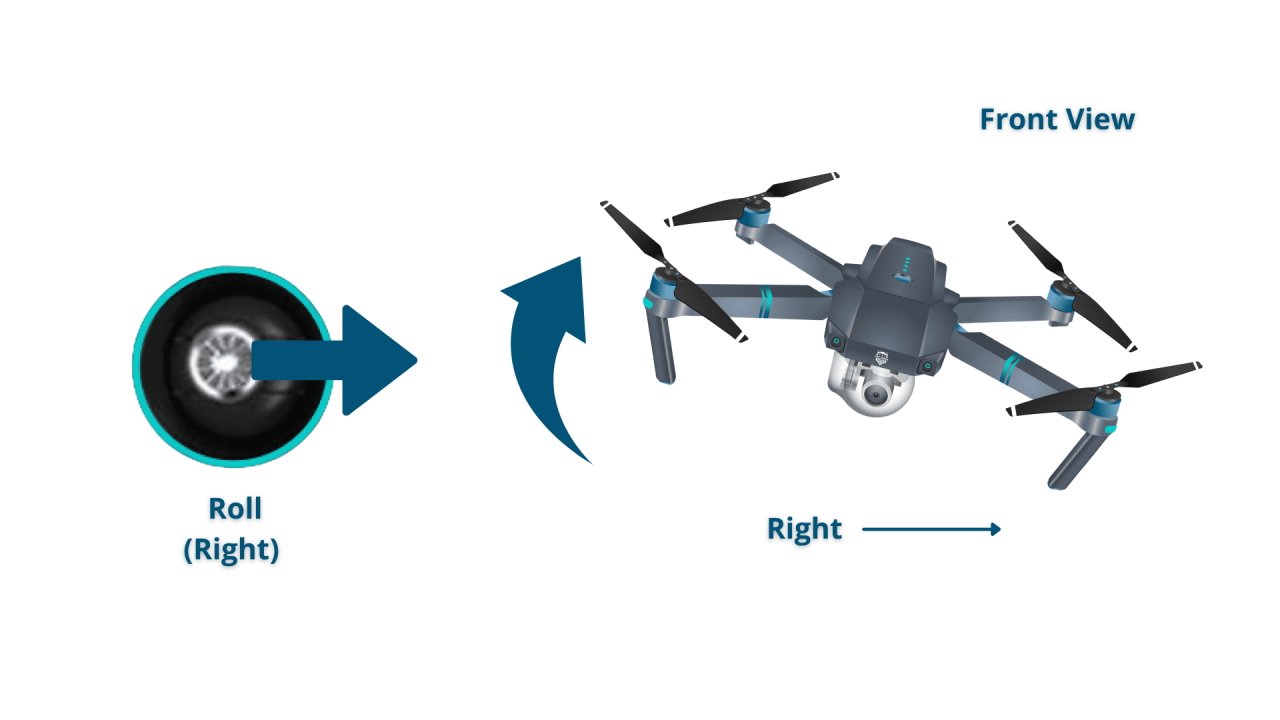
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones utilize a control system based on four primary axes: throttle (controls altitude), yaw (controls rotation around the vertical axis), pitch (controls movement forward and backward), and roll (controls movement left and right). Understanding how these controls interact is essential for smooth and controlled flight. Many drones offer different levels of control sensitivity, allowing for customization based on experience and flight conditions.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer various flight modes to cater to different skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, providing a more stable and forgiving flight experience. Sport mode, on the other hand, allows for faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, but requires more skill and experience. GPS and Attitude modes provide different levels of stabilization and autonomy.
Drone Navigation Methods
GPS and visual positioning are the primary methods of drone navigation. GPS uses satellite signals to determine the drone’s location, enabling precise positioning and autonomous flight features. Visual positioning relies on cameras and sensors to track the drone’s surroundings, allowing for stable flight in GPS-denied environments. Hybrid systems combine both methods for optimal performance.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle to keep the drone at a consistent altitude.
- Landing: Gradually decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Effective flight planning is crucial for safe and efficient drone operations. This involves considering various factors and utilizing appropriate tools for mission execution.
Safe and Effective Flight Planning
Before each flight, consider weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and potential hazards. Check for any Notices to Airmen (NOTAMs) that might affect your flight plan. Ensure that your chosen flight area is safe and free from obstacles. Always have a backup plan in case of unexpected issues.
Creating a Flight Plan

Many drone-specific software applications and mobile apps allow for the creation of detailed flight plans. These tools enable you to define waypoints, altitudes, and other flight parameters. This allows for precise and repeatable flight paths, particularly useful for tasks such as aerial photography, surveying, or inspections.
Types of Drone Missions

Drones are used for a variety of missions, including aerial photography and videography, inspections of infrastructure (bridges, power lines), search and rescue operations, and delivery services. The choice of drone and flight plan will depend heavily on the specific mission requirements.
Drone Mission Checklist
- Pre-flight checks (battery, GPS, etc.)
- Flight execution (following planned route)
- Post-flight procedures (data download, drone storage)
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of your drone. This section covers routine maintenance tasks and troubleshooting common issues.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance includes inspecting propellers for damage, cleaning the drone body and sensors, checking battery health, and updating firmware. The frequency of these tasks depends on the usage frequency of the drone. Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities can help to track potential issues and ensure timely interventions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include low battery life (due to age or overuse), signal loss (interference or distance), motor failures (physical damage or wear), and GPS issues (satellite interference or malfunction). Understanding the potential causes of these issues is important for effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Troubleshooting techniques involve systematically checking components, replacing faulty parts, and seeking assistance from the manufacturer or experienced drone operators. In many cases, simple solutions, such as re-calibrating the compass or replacing a battery, can resolve the issue. For more complex problems, professional assistance might be necessary.
Drone Maintenance Schedules
| Frequency of Use | Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Visual inspection | After each flight | Check for physical damage |
| Weekly | Battery health check | Once a week | Use a battery analyzer |
| Monthly | Firmware update | As needed | Check for updates from the manufacturer |
| Annually | Comprehensive service | Once a year | Professional service may be needed |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally and responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations. This section highlights key aspects of legal compliance.
Key Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary significantly by country and region. It is crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations that apply to your location. These regulations often cover areas such as registration, licensing, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
In many jurisdictions, operating a drone commercially or for certain types of operations requires obtaining specific permits or licenses. The process for obtaining these permits typically involves submitting an application and demonstrating compliance with safety regulations.
Airspace Restrictions and Limitations
Airspace restrictions are common, particularly around airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. These restrictions often limit the altitude or geographic area where drones can operate. Failing to adhere to these restrictions can result in penalties.
Prohibited or Restricted Scenarios
Drone operation is often prohibited in areas such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and near critical infrastructure. Flying over crowds, private property without permission, and operating at night without appropriate lighting are also typically restricted or prohibited.
Advanced Drone Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers, camera techniques, and data processing for enhanced drone operation and aerial content creation.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Waypoint navigation allows for pre-programmed flight paths, enabling autonomous missions. Automated flight features, such as follow-me mode or point-of-interest orbits, enhance operational efficiency and creative possibilities. Mastering these techniques requires practice and a thorough understanding of the drone’s capabilities.
Camera Settings and Techniques
Understanding camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is vital for capturing high-quality aerial footage. Different settings are optimal for various lighting conditions and desired effects. Proper exposure and white balance are crucial for achieving professional-looking results.
Data Processing and Post-Processing
Raw aerial images and videos often require post-processing to enhance quality and correct for distortions or color imbalances. Software applications offer tools for adjusting exposure, contrast, sharpness, and color grading. Advanced techniques, such as photogrammetry, can be used to create 3D models from aerial imagery.
Effect of Different Camera Angles
A high-angle shot provides a wide overview of the scene, while a low-angle shot emphasizes scale and perspective. Side-angle shots offer a different viewpoint and can highlight specific details. The choice of camera angle significantly impacts the mood and message conveyed in aerial photography and videography.
Drone Photography and Videography
This section focuses on capturing compelling aerial shots and creating high-quality aerial media.
Best Practices for Composing Aerial Shots, How to operate a drone
Effective aerial composition involves considering the rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing to create visually appealing images. Understanding perspective and using natural elements to enhance the composition are crucial for capturing dynamic and engaging shots.
Optimizing Image Quality with Camera Settings
Adjusting aperture, shutter speed, and ISO allows for control over depth of field, motion blur, and image brightness. Understanding the interplay of these settings is crucial for achieving optimal image quality in various lighting conditions. Experimentation and practice are key to mastering these techniques.
Stabilizing Footage and Minimizing Camera Shake
Using a gimbal or other stabilization system significantly reduces camera shake, resulting in smoother and more professional-looking footage. Post-processing techniques, such as image stabilization software, can further enhance the quality of shaky footage.
Workflow for Editing and Post-Processing
A typical workflow involves importing footage, color grading, adding effects, and exporting the final product. Using professional editing software allows for advanced techniques such as motion tracking, keyframing, and compositing. Efficient workflow organization is key to producing high-quality aerial videos and photos efficiently.
Successfully operating a drone requires a blend of technical skill, responsible decision-making, and a thorough understanding of applicable regulations. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of these critical aspects, equipping you with the knowledge to fly safely and effectively. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and maximizing the potential of your drone.
Embrace the possibilities, fly responsibly, and capture stunning aerial perspectives with confidence.
Answers to Common Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from beginner to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your drone piloting skills.
This will help ensure you can operate a drone responsibly and efficiently.
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, attempt to initiate the return-to-home function if available. If that fails, immediately contact local authorities.
How do I ensure my drone footage is stable?
Use a drone with good stabilization features, fly smoothly, and consider using post-processing software to further stabilize your footage.